VFDs (Vacuum Fluorescent Displays) are high contrast displays that can display 7-segment numerals, multi-segment alphanumeric characters or a dot matrix pattern. These display types are typically colored green, bright and perform well in both dark and full sunlight environments. VFDs use a self-emitting fluorescent light allowing them to operate in extreme cold and hot temperatures. VFDs are commonly used in consumer based electronics such as car radios, ovens and DVD/Blue-ray players.
Newhaven Display offers both glass and module type VFDs. The glass VFDs are available in standard sizes and come as either 7-segmented, alphanumeric or Dot Matrix displays.
Newhaven Display’s module VFDs are available in standard sizes and feature a PCB board with a built-in controller. These displays can be used as compatible replacements for LCD or OLED modules. Like the glass VFDs, they are available as alphanumeric or Dot Matrix displays. Newhaven Display offers custom design for both the glass and module type VFDs.
VFDs are composed of a hot cathode filament, anode segments coated with phosphor and grids within a vacuum sealed glass encasement. The filament is made up of alkaline coated tungsten wires which enable the display to emit light.
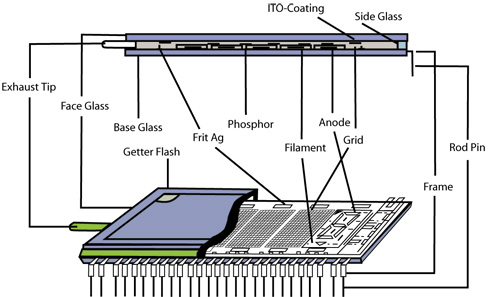
Cathode- The Cathode (Filament) is the barium oxide coated tungsten wire which is heated by the external power source to approximately 600°C and emits free thermal electrons.
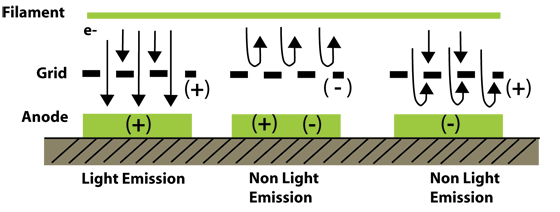
Grid- The Grid is a metal mesh over the phosphor coated anodes and controls the electrons emitted from the cathode.
Electrons- In the case of non-light emission, electrons from the cathode are either blocked by the grid with a negative potential, or passed through the grid and repelled by the negative potential anode. In the case of light emission, electrons from the cathode are accelerated by the positively charged grid toward the positively charged anode. The phosphor on the anode emits luminous radiation when excited by electrons.
When heat generated by a power supply is applied to the tungsten wires, the alkaline coating emits electrons. These electrons are controlled and diffused by the thin metal grids within the display. When these electrons come in contact with the phosphor coated plates they emit light.
Color filters can be applied to any VFD to change the overall look of the display. These filters alter the color of the VFD and increase the contrast ratio, as well as act as a protective shield.
Some colors available include:
